Search Results for: dna repair
Recombination DNA repair
Recombination DNA Repair Definition Recombination DNA repair is a biological reparative process in response to DNA damage... Read More
Deoxyribonucleic acid
Deoxyribonucleic Acid (DNA) Definition A nucleic acid refers to any of the group of complex compounds made up of linear... Read More
Nucleosome
Nucleosome Definition Every organism is made of deoxyribonucleic acid, also known as DNA. DNA is made up of numerous... Read More
How cell fixes DNA damage
DNA repair strategies DNA is crucial to life. It carries the fundamental blueprint for the proper functioning of a cell.... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA
Mitochondrial DNA Definition noun plural: mitochondrial DNAs The genetic material in the mitochondrion that carries code... Read More
Genetic Information and Protein Synthesis
Genetic Code Genes are sequences of DNA nucleotides that carry and transmit the information specifying amino acid sequences... Read More
Dna repair
Dna repair (Science: molecular biology) Each cell has a series of special enzymes to correct the errors in dna structure and... Read More
Chromatids
Chromatid Definition Chromatids are found inside our cells. Chromatids are condensed chromosomes distinguishable during... Read More
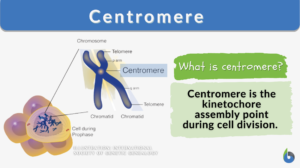
Centromere
Centromere Definition Centromere is defined as the point of attachment for the sister chromatids generated after DNA... Read More
Sister chromatids
Sister Chromatids Definition Sister chromatids are defined as the two identical copies of a single replicated chromosome... Read More
Pyrimidine
Definition noun plural: pyrimidines py·rim·i·dine, py·rim·i·dine A heterocyclic aromatic compound that presents as... Read More
Nucleobase
Definition noun plural: nucleobases (biochemistry) The base in the nucleic acid, e.g. purines and pyrimidines Details ... Read More
Silent mutation
A mutation is a change in the nucleotide sequence of a gene or a chromosome. When there is only one nucleotide involved, it... Read More
DNA polymerase I
Definition noun The first known DNA polymerase, encoded by polA gene, and is involved in DNA replication in... Read More
Thymidine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and a... Read More
Denaturation
Denaturation Definition In biochemistry, denaturation is defined as a process in which a molecular structure deviates from... Read More
Cell division
Cell division is a biological process by which a parent cell duplicates its cell contents and divides to give rise to two or... Read More
Thymidine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and three... Read More
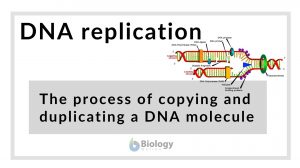
DNA replication
DNA Replication Definition DNA replication is the process of copying and duplicating a DNA molecule. The process is carried... Read More
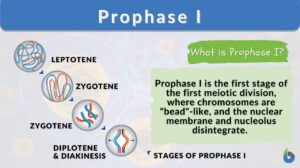
Prophase I
Organisms all use mitosis to create more cells in the body. Meiosis, a similar process, is used in some organisms to undergo... Read More
Thymidine diphosphate
Definition noun plural: thymidine diphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of thymine, deoxyribose and two... Read More
Uridine triphosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine triphosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and three phosphate... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
Uridine monophosphate
Definition noun plural: uridine monophosphates (biochemistry) A nucleotide composed of uracil, ribose and a phosphate... Read More
Mitochondrial DNA – hallmark of psychological stress
We often hear that stress can be unsettling as it could make us ill when it becomes chronic and overwhelming. However, is... Read More
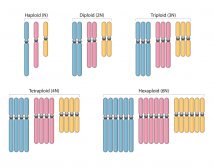
Polyploidy
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D. Polyploidy Polyploidy is defined as the state of being polyploid, which... Read More